While taking the beautiful vs kitsch photograph, there are several factors which should be considered. Firstly, one has to define what is beautiful and what is kitsch? By researching the meanings of these two terms we were be able to look for beautiful and kitsch in the campus. What we did until finding the correct object is data collecting. We searched for their meanings and tried to find out in which place in the campus we can find the beautiful and the kitsch. Then, when we are well informed enough, we were be able to find the beautiful and the kitsch. While trying to take photos in the campus, distinguishing the beautiful and kitsch from any other objects is observation. Since art may depend on person’s point of view; in photographic art, abstraction is important. We decided on the beautiful and the kitsch according to our thoughts. Maybe we understand some object’s value different than it really is. This is abstraction. And during all this process we have awareness; that we know what we are doing from beginning to end.
29 Mayıs 2008 Perşembe
MIDTERM - 2 Question 9 ==> Beautiful vs Kitsch correlated with 'data collection', 'observation', 'abstraction' and 'awareness'
28 Mayıs 2008 Çarşamba
Question 8 ==> What is Iterative & Sequential ?
Iterative: It is an adjective used to define a procedure that involves repetition of steps to achieve desired outcome.
References:
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=iterative
==>http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/iterative
Sequential: If something is sequential, then there are other things coming before or after it.
References:
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=sequential
Question 7 ==> What is Event & Process & Life Cycle ?
Event: An event is the occurrence of a situation. However, in a more formal form, it is a phenomenon that changes the application’s state. An event attracts attractions of people that are affected by it.
References:
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=event
==>http://ansiklopedi.turkcebilgi.com/olay
==>Çetinkaya, Ferda
==>Industrial Engineering Terminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA,
Process: Process is the time duration when the ideas are arranged one after another until they reach a conclusion. Shortly, it is organized set of activities. In work life, it is a particular course of action intended to achieve a result.
References:
==>http://www.google.com/define:process
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=dizili%FE
==>http://ansiklopedi.turkcebilgi.com/süreç
Life Cycle: In general form, it is the series of forms or stages of development that a plant animal or something goes through from the beginning of its life to the end. But in industry, in a different form, ‘life cycle’ is the time from the beginning of the systems project to the replacement of the system. This includes the time that the system will be operational as well as the time needed to develop and implement the system.
References:
==>http://www.google.com/define:life%20cycle
27 Mayıs 2008 Salı
Question 6 ==> What is validation/validity, significance, reliability, relevance/relavent ?
==>a) ==>i) Validation: It is a commonly used word in engineering especially in industrial engineering. It means whether a product’s needs are answered by users or customers. This can also involve a combination of methods, such as letting domain experts verify the knowledge in the knowledge base, using automated procedures to check the system for consistency, and applying the system to a larger number of test cases.
ii) Validity: Validity refers to the degree to which a study accurately reflects or assesses the specific concept that the researcher is attempting to measure.
References:
==>http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/validity.html
==>Çetinkaya, Ferda
==>Industrial Engineering Terminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA,
==>http://writing.colostate.edu/guides/research/relval/pop2b.cfm
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Validity
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=validity
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=validation
==>b) ==>Significance: The significance of something is the importance that it has. It is usually because it will have an effect on a situation or shows something about a situation.
References:
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Significance
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=significance
==>Çetinkaya, Ferda
==>c) ==>Reliability: Reliability is simply the dependability of a product. But, in more complex form, it is the ability of an equipment, machine, or system to consistently perform its intended or required function or mission, on demand and without degradation or failure. It is also the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time.
References:
==>Industrial Engineering Terminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA,
==>Çetinkaya, Ferda
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reliability
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=reliability
==>d) ==>i) Relevance: Relevance is a subjective measure of how well a document satisfies the user's information need. In fact, it is also a criterion used in evaluating the quality of information. Something’s relevance to a person depends on how relevant this person to this situation. So, we should also define ‘relevant’.
ii) Relevant: Something that is relevant to a situation or person is its importance or relevance to that situation.
References:
==>http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/relevant
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relevant
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=relevant
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relevance
==>Industrial Engineering Terminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA,
==>Çetinkaya, Ferda
Question 5 ==> What is model & snowball effect & waterfall diagram ?
References:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model
- http://ansiklopedi.turkcebilgi.com/model
- http://www.toplumdusmani.net/modules/wordbook/search.php
- http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=anlaml%FD
- Çetinkaya, Ferda Can. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,Ankara,2008
- Industrial Engineering Terminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA, USA, 1989
b) Snowball Effect: It is a term that explains the process of how small situations grows up and becomes a huge condition. This expression comes from nature. On the snowy top of a hill if one pulls a small snowball down, theoretically it during the process while it goes on, snowball becomes larger and larger and in the end, it becomes a huge snowball.
References:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snowball_effect
- http://www.britannica.com/search?query=snowball+effect&ct=&searchSubmit.x=0&searchSubmit.y=0
c) Waterfall Diagram: Waterfall diagrams are a special type of floating column charts. A typical waterfall diagram shows how an initial value is increased and decreased by a series of intermediate values, leading to a final value. An invisible column keeps the increases and decreases linked to the heights of the previous columns. They are useful for showing how components build up to a total or to show the progression from a larger number to a smaller number.
References:
- http://www.kan.org/tips/powerpoint_waterfall.php
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waterfall_plot
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waterfall_chart
- Çetinkaya, Ferda Can. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,Ankara,2008
25 Mayıs 2008 Pazar
Question 4 ==> What is Strategy & Plan & Control
==>a) ==>Strategy: Strategy is a long term activict which is determined before the action, aimed to reach a specific target made by individuals or companies or foundations… In the Greek language it means “general’s art”, since in history it is mostly used in army. Strategies are used to make the problems easier to understand and solve.
References:
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strategy
==>http://www.toplumdusmani.net/modules/wordbook/search.php
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=strategy
==>http://www.turkcebilgi.com/strateji
==>Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
==>Industrial Engineering Therminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA,
==>b) ==>Plan: Plans are made before the action with the aim of concluding a work, an idea or a task. Plans are written or drawn or pictured with detailed points of the work in order not to fail during to action. In other words, plans show the route of the work.
References:
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plan
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=plan
==>http://www.toplumdusmani.net/modules/wordbook/search.php
==>http://www.turkcebilgi.com/plan
==>Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
==>Industrial Engineering Therminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA,
==>c) ==>Control: It is the action of checking whether the work is done in its expected route correctly. Control is one of the managerial functions like planning, organizing, staffing and directing. It is an important function because it helps to check the errors and to take the corrective action.
References:
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=Denetlemek
==>http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=control
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Control_(management)
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Control
==>Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
Question 3 ==> What is theory & hypothesis & paradigm
a) Theory : It is the coherent group of general assumptions. Theory is the body of principles which belongs to a certain subject, speculation, or hypothesis. This can be said that a theory it is a deep rooted hypothesis. Thus, theories allow scientists to make predictions about as yet unobserved phenomena.
References:
==>Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
==>Mehdi Khasrow-Pour. Dictionary of Information Science and Technology,
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theory
==>http://www.toplumdusmani.net/modules/dictionary/detail.php?id=1805
==> http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=k%F6kle%FEmi%FE
==>b) Hypothesis : Hypothesis is the temporary solution to a problem. It is a suppositional assumption which is made in order to draw out and test its logical or empirical consequences. If a hypothesis is proved wrong then it is leaved and a proper hypothesis is set.
References:
==> Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
==>Mehdi Khasrow-Pour. Dictionary of Information Science and Technology,
==> http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothesis
==> http://www.toplumdusmani.net/modules/wordbook/search.php
==> http://www.seslisozluk.com/?word=hypotheis
==>http://ansiklopedi.turkcebilgi.com/Hipotez
==>c) Paradigm : It is the general point of view of individuals groups and publics. Any tip or model that can be a criterion is a paradigm of that subject. A paradigm is the clear and typical example of something. Productions are made according to a paradigm, since paradigms are simple models of something.
References:
==> Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
==> http://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paradigma
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paradigm
==> http://www.turkcebilgi.com/paradigma
==> http://www.toplumdusmani.net/modules/wordbook/search.php
Question 2 ==> What does method & methodology mean?
==>a) ==>Method: Method can be explained as a way of approaching a situation. How one thinks, how one gets its target, or how one handles a problem is one’s method. In other words, a method is a procedure of doing works.
References:
-Mehdi Khasrow-Pour. Dictionary of Information Science and Technology. Information Resources Management Association, NY,
-
- Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimleri Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Method
b) Methodology: Methodology is a consistent and suited set of modeling methods and the analysis of the principles of methods, rules, and assumptions. Methodology provides procedures to apply the constructs of a modeling rule.
References:
-Mehdi Khasrow-Pour. Dictionary of Information Science and Technology. Information Resources Management Association, NY,
-Çetinkaya,F.C. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimleri Sözlüğü , TMMOB,
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Method
- http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/methodology
Question 1 ==> What is a problem?
A problem is a situation which makes someone to go in uncertainty. A problem puts barriers to individuals who want to get their target. In such a situation people do not know quickly what actions to accomplish a problem.
For industrial engineers on the other hand, a problem is the reason for their existence.
References:
==>Çetinkaya, Ferda Can. İngilizce Türkçe Endüstri Mühendisliği ve Mühendislik Yönetimi Terimler Sözlüğü , TMMOB,Ankara,2008
==>Industrial Engineering Terminology. Management Pres Institute of Industrial Engineers GA, USA, 1989
==>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Problem
28 Nisan 2008 Pazartesi
Beautiful vs Kitsch
30 Mart 2008 Pazar
Origins Of Engineering & Beginning of Engineering Education
Beginning of Engineering Education
People who organized construction of the Great Pyramid, 5000 years ago, richly deserves to be called an engineer. (or ancient engineer). But the term has only been in general use for 200 years; -- since universities began training people to build things. First engineer workshops were done in armies. By the mid-1600s, artillery and fortifications had grown so complex that armies began training officers in math and mechanics. That gradually turned into civil engineering. In 1775, King Louis XV of
However most importent development in engineering are industrial revolutian and steem engines and after these many types of engineering appeared. Then,universities began to give engineering education to their students.The first schools of engineering was founded in
Origins Of Engineering
In prehistoric times, men and women had to be ingenious in order to survive hunger, enemies, climate and, later, the tyrrany of distance. So there have always been 'engineers' around, many of whom were involved in activities we would not associate with engineering today but, rather, with hunting, farming, fishing, fighting, implement- and tool-making, transportation and many other things.
From around 3000 BC, the pace of development quickened. After simple tools came the development of wedges, wheels and levers, the use of animals to carry and draw loads and of fire to work metals, the digging of irrigation canals, and
The Greeks - the inventors - made significant contributions in the 1000 years that straddled the BC-AD divide. They produced the screw, the ratchet, the water wheel and the aeolipile, better known as Hero's turbine. The Romans - the improvers and adapters - did likewise, building fortifications, roads, aqueducts, water distribution systems and public buildings across the territories and cities they controlled. At the other end of the world, the Chinese have been credited with the development of the wheelbarrow, the rotary fan, the sternpost rudder that guided their bamboo rafts and, later, their junks. They also began making paper from vegetable fibres - and gunpowder.
Sources:
http://www.uh.edu/engines/epi1107.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Engineering#History
http://www.new-sng.com/history.cfm
What Engineers Do?

Engineers are concerned with the creation of structures , devices, and systems for human use. They are also problem solvers (Especially Industrial Engineers). Their work is often the link between a scientific discovery and its application. Many engineers develop new products. During this process, they consider several factors. For example, in developing an industrial robot, engineers precisely specify the functional requirements; design and test the robot's components; integrate the components to produce the final design; and evaluate the design's overall effectiveness, cost, reliability, and safety. This process applies to the development of many different products, such as chemicals, computers, power plants, helicopters, and toys.
Types Of Engineers
=====>Electric&Electronic Engineering
This branches of engineering is the largest one of all. Electric engineering is concerned with electrical devices, currents and systems. It also deals with the study and application of , electricity electronics and electromagnetisim.
=====>Mechanical Engineering
It is one of the largest areas of engineering activity. In some cases it is called “medicine of engineering.” Mechanical engineers concern with machinery power and manufacturing or production.
=====>Civil Engineering
Civil engineering concerns with the design, construction and maintenance of the physical and natural built environment containing buildings we live the transportation facilities we use the water we drink, and the drainage and sewerage systems that are necessary to our health and well-being.
=====>Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering involves the application of the chemistry, physics and engineering to the design and operation of plants for the production of materials that undergo chemical changes during the manufacture.
=====>Industrial Engineering
Industrial Engineers are concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, material and energy ,in the production of either goods or devices.
Industrial engineering is also known as , system engineering, production engineering, operation s management, manufacturing engineering or manufacturing systems engineering.
Whereas most engineering disciplines apply skills to very specific areas, industrial engineering is applied in virtually every industry. Industrial Engineering is at the heart of the systems that are essential to our society. From airlines to online retailers, from hospitals to manufacturers, from telecommunication companies to world-wide shipping companies, industrial engineers design solutions to improve the performance of complex systems of people, technology, and information.
Industrial engineers perform time and motion studies of workers, set standards of work performance, and propose new improved work methods to increase productivity.
=====>Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace Engineering is concerned with all aspects of vehicular flight at all speeds and altitudes. It covers all phases of research, design, and development in this broad area.
=====>Agricultural Engineering
Agricultural Engineering Associates was formed to fill the void for technical engineering services at the production of agriculture grassroots.
=====>Material Engineering
The term material engineering refers in a general way to a group of engineering specializied that are concerned with the development, production, fabrication, and use of materials in specific technologies.
=====>Textile Engineering
Textile engineers deal with the planning design and operation of the manufacturing plants in the textiles industry.
=====>Environmental Engineering
Environmental engineering deals with air pollution control, industrial hygiene, radiation protection, hazardous waste management, toxic materials control, water supply, waste water management, storm water management, solid waste disposal, public health, and land management.
Sources:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_engineering
http://industrialengineering.dal.ca/
http://www.aaee.net/Website/Careers
Introduction to Engineering by Paul Wright
Engineering As a Profession

In order to use the materials and forces of nature for the benefit of people, engineering applies the knowledge of mathematics and natural sciences with discretion and judgment as a profession.
It differs from other professions in several ways:
In the type of service provided, in the training requirements for its practitioners, in the diversity of its leadership, and in the lack of uniformity, and rigidity in its registration laws.
In contrast to other professions engineering tend to create machines, structures, processes and other products for the use of group of people; not individually.
Although it differs significantly from other types of professions in several aspects, engineering possesses those attributes that characterize a profession;
- It satisfies an priceless and beneficial need.
- It requires the exercise of foresight and judgment and is not subject to normalization.
- It contains a type of activity that is conducted on a high intellectual plane based on knowledge and skills which are not commonly have by the general society.
- It has group consciousness for the promotion of knowledge and professional and rendering social services.
- It has a legal status and requires well-formulated standards of permission
Sourcess:
Introduction to engineering-by Paul H. Wright
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Engineering
My Preference

If I were one of these VIP’s, I would like to be Frank Bunker Gilbreth. There are several reasons for this choice. First of all, he was a good father and a husband; although he had twelve children, he could be a very good father for all of his children. He could share time with his children even if he had very much work to do. Secondly, he was a good explorer and engineer although he did not graduate from a college. He worked on efficiency and tried to improve the work done per unit very beneficially. He did not forget that his work area contains “human factor”. The progress that he did in work place did not force workers to work harder or work much time. On the contrary his works of efficiency improved the conditions of employees. At this point, F.B.Gilbreth differs from Frederic Taylor, Henry Ford and Henri Fayol.
Maximillian Carl Emil Weber(1864-1920)

Maximillian Carl Emil Weber who was born in 1864 in Germany was considered by many to be the father of sociology. He was also a political economist. According to Max Weber sociology is a science that is concerned with a social action and the course and/or consequences of the action. In addition to sociology econmoy and politics, he touched on religion. It can be said that his most precious work is the Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism. In this case, in many aspects of social economy, he disagreed with Karl Marx who was the father of Communism. Weber states that "economics is not a science of nature and its qualities, but of people and their needs". One can say about Weber's theory of social economics that, it helps to construct a dialogue between economists and sociologists.
In Weber’s Sociology there are four major types of social action; which are;
v Men may engage in purposeful or goal-oriented rational action.
v Men’s rational action may be value-oriented.
v Men may act from emotional or affective motivations
v Men may engage in traditional action.
http://www.6sociologists.20m.com/weber.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Max_Weber#Sociology_of_religion
http://cepa.newschool.edu/het/profiles/weber.htm
Lilian Moller Gilbreth(1978-1972) & Frank Bunker Gilbreth(1868-1924)

 Lillian Moller Gilbreth
Lillian Moller Gilbrethwas the industrial & organizational psychologist who was also working as a first woman engineer holding a PhD. Lillian and Frank were true partners from the beginning. Her husband Frank B. Gilbreth was a businessman and Lillian was a industrial psychologist. This enabled the couple work in harmony, and made big successes in workplace. They both became passionate about finding the "one best way" to perform any task in order to increase efficiency and productivity in industry. For Frank Gilbreth, efficiency is the most basic thing in the workplace. He was not an educated person whereas he was passionate about doing his job in best way, and even in his work time he was thinking about how to improve quality of the work he was doing. He had a constructor company an he was asking both himself and the people around him to develop efficiency of labors. As a result of his thoughts and experiments he could improve the effectiveness of a worker 200% than before. Moreover, in this case, the workers were not doing much hard work or not working for much time. In deed, they were doing their job in the most effective way and in the most effective conditions. Mr. Gilbreth for years has closely wached workers at tasks of all kinds; he has discovered how much they lose by maving unprofitably hither and thither, by neglecting to take the shortest and easiest paths.
F.B.Gilbreth also worked on many scientific management issues such as:
Field System, Concrete System, Bricklaying System, Motion Study, Primer of Scientific Management, The Psychology of Management (with his wife Lillian Gilbreth), and Fatigue Study.
Gilbreth’s studies on industrial engineering mostly affected from
After F.Gilbreth’s dead Hİs wife Moller Gilbreth tried to continue his husbands jobs, but she could not be so successful. On the other hand, she was one of the consultants of presidents Kennedy, Eishenhower, Roosevelt and Hover.
In 1946 their children Frank Jr. Gilbreth and Ernestie Gilbreth wrote a book "Cheaper by the Dozen" explaining the family life of the family.

Sources:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frank_Bunker_Gilbreth
http://www.webster.edu/~woolflm/gilbreth2.html
http://www.sdsc.edu/ScienceWomen/gilbreth.html
www.ergonomia.org.pl/bios/E-bio-Gilbreth.pdf
ABRAHAM MASLOW (1908-1970)

Abraham Maslow was a Jewish-American psychologist who is accepted as the father of humanistic psychology. Since he was the only Jewish boy in his childhood, he felt very much loneliness. And this loneliness forced him to find his refuge in books, and would be a fundamental factor that will make him study humanistic psychology later. His most famous work for human psychology is admittedly “Pyramid of Hierarchy of Needs”. This pyramid consists of five parts first of which starts from bottom as “psychological needs” and finishes as “self actualization”.
***Firs step of the pyramid is Biological and Physiological needs – such as, air, food, drink, shelter, warmth, sex, and sleep.
***The second step consist of Safety needs – like, protection from elements, security, order, law, limits, stability.
***Belongingness and Love needs is the third step of the pyramid –containing, work group, family,
affection, relationships.
***The fourth step of the pyramid is Esteem needs – consisting of, self-esteem, achievement, mastery, independence, status, dominance, prestige, managerial responsibility
***Self-Actualization needs is the final and the top step of the pyramid- realizing personal potential, self-fulfillment, seeking personal growth and peak experiences...
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs can also be adapted to workplace as in the following form:
*Physiological needs: Providing lunch breaks, resting breaks, and waging that are sufficient to purchase the essentials of life.
*Safety Needs: Providing a safe working environment, retirement benefits, and job security.
*Social Needs: Creating a sense of community via team-based projects and social events.
*Esteem Needs: Recognizing achievements to make employees feel appreciated and valued. Offering job titles that convey the importance of the position.
*Self-Actualization: Providing employees a challenge and the opportunity to reach their full career potential.
Sources:
http://motivationcentre.blogspot.com/2006/03/implications-of-maslows-hierarchy-of.html
http://www.valuebasedmanagement.net/images/picture_maslow.jpg
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maslow%27s_hierarchy_of_needs
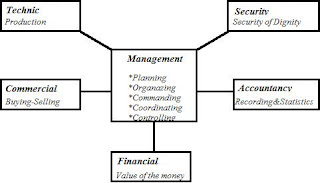
Henri Fayol (1841-1925)

Henri Fayol was an French engineer and management theorist who was born in
Here is the chart that explains the management principles and steps of Henri Fayol.
Sources:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henri_Fayol
http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia
Genel ve Endüstriyel Yönetim -HENRI FAYOL- ADRES Yayınları
17 Mart 2008 Pazartesi
Frederick Winslow Taylor(1856-1915)

Frederick Winslow Taylor (March 20, 1856 - March 21, 1915), widely known as F. W. Taylor, was an American mechanical engineer who sought to improve industrial efficiency. A management consultant in his later years, he is sometimes called "the father of scientific management." He was one of the intellectual leaders of the Efficiency Movement and his ideas, broadly conceived, were highly influential in the Progressive Era.
By far the most influential person of the time and someone who has had an impact on management service practice as well as on management thought up to the present day, was F. W. Taylor. Taylor formalized the principles of scientific management, and the fact-finding approach put forward and largely adopted was a replacement for what had been the old rule of thumb.
Objectives of Scientific Management
The four objectives of management under scientific management were as follows:
- The development of a science for each element of a man's work to replace the old rule-of-thumb methods.
- The scientific selection, training and development of workers instead of allowing them to choose their own tasks and train themselves as best they could.
- The development of a spirit of hearty cooperation between workers and management to ensure that work would be carried out in accordance with scientifically devised procedures.
- The division of work between workers and the management in almost equal shares, each group taking over the work for which it is best fitted instead of the former condition in which responsibility largely rested with the workers. Self-evident in this philosophy are organizations arranged in a hierarchy, systems of abstract rules and impersonal relationships between staff.
F.W. Taylor's contribution to organizational theory
This required an organization theory similar for all practical purposes to that advocated by those organizational theorists who followed. These theorists developed principles of management, which included much of
His framework for organization was:
- clear delineation of authority
- responsibility
- separation of planning from operations
- incentive schemes for workers
- management by exception
- task specialization
Sources:
http://www.accel-team.com/scientific/scientific_02.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frederick_Winslow_Taylor